Song, H., J. Marshall, M.J. Follows, S. Dutkiewicz, and G. Forget. Source waters for the highly productive Patagonian shelf in the southwestern Atlantic. Journal of Marine Systems – early online edition.
Category Archives: Diversity and Biogeography
Keeping Things the Same
The elemental composition of organic matter is remarkably constant throughout the world’s oceans, but phytoplankton are known to take up nutrients and carbon in quite variable ratios depending on light and nutrient conditions.
In a paper published online in the journal Global Biogeochemical Cycles last month, Darwin Project researchers David Talmy (MIT), Christopher Hill (MIT), Anna Hickman (Univ. of Southampton, England), and Mick Follows (MIT), in a collaboration with Adam Martiny (Univ. of California, Irvine), report on their work seeking to understand what ecosystem factors could cause the elemental composition of organic matter to remain stable and relatively constant (homeostatic), even when the phytoplankton can have quite variable composition. Continue reading Keeping Things the Same

Ocean acidification may cause dramatic changes to phytoplankton
Study led by principal research scientist Stephanie Dutkiewicz finds many species may die out and others may migrate significantly as ocean acidification intensifies. Continue reading Ocean acidification may cause dramatic changes to phytoplankton
Dutkiewicz, S., J.J. Morris, M.J. Follows, J. Scott, O. Levitan, S.T. Dyhrman, and I. Berman-Frank, 2015, Impact of Ocean Acidification on the Structure of Future Phytoplankton Communities. Nature Climate Change, doi: 10.1038/nclimate2722

Uncovering a Diverse Invisible Ocean World
Read this story at oceans.mit.edu
Tara Oceans, an international consortium of researchers that explored the world’s oceans in hopes of learning more about one of its smallest inhabitants, reported their initial findings this week in a special issue of Science. Plankton are vital to life on Earth—they absorb carbon dioxide, generate nearly half of the oxygen we breathe, break down waste, and are a cornerstone of the marine food chain. Now, new research indicates the diminutive creatures are not only more diverse than previously thought, but also profoundly affected by their environment. Continue reading Uncovering a Diverse Invisible Ocean World
Villar, E., Farrant, G.K., Follows, M.J., et al, 2015, Environmental characteristics of Agulhas rings affect interocean plankton transport. Science, Vol. 348 no. 6237, doi: 10.1126/science.1261447
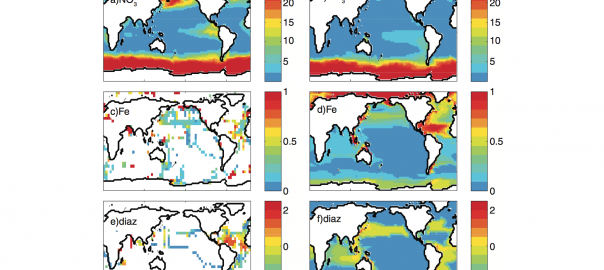
Life on the Edge – How shifting marine province boundaries could provide a new metric for global change
In their new competition theory paper, appearing in the 2014 issue of Biogeosciences, Dutkiewicz et al examine the sensitivity of the biogeography of nitrogen fixers to a warming climate and increased aeolian iron deposition in the context of a global earth system model. Continue reading Life on the Edge – How shifting marine province boundaries could provide a new metric for global change
Dutkiewicz, S., Ward, B. A., Scott, J. R., and Follows, M. J. (2014) Understanding predicted shifts in diazotroph biogeography using resource competition theory, Biogeosciences, 11, 5445-5461, doi: 10.5194/bg-11-5445-2014.
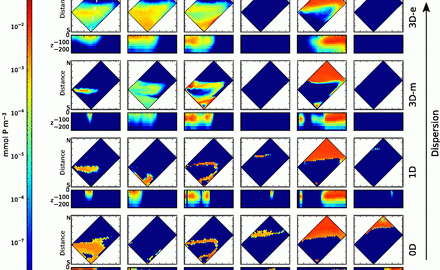
Mixing Down Diversity
Phytoplankton are an extremely diverse set of floating, microscopic organisms, which are freely transported by water movements (current, eddies, etc.) and make up the base of the oceanic food web. This work, published in the September issue of Limnology & Oceanography: Fluids & Environments, explores how their diversity is affected by dispersal by different scales of motions in the ocean. Continue reading Mixing Down Diversity
Levy, M., O. Jahn, S. Dutkiewicz, and M.J. Follows (2014), Phytoplankton diversity and community structure affected by oceanic disperal and mesoscale turbulence, Limnology and Oceanography: Fluids and Environment, 4, 67-84, doi: 10.1215/21573689-2768549.